Solid phase extraction
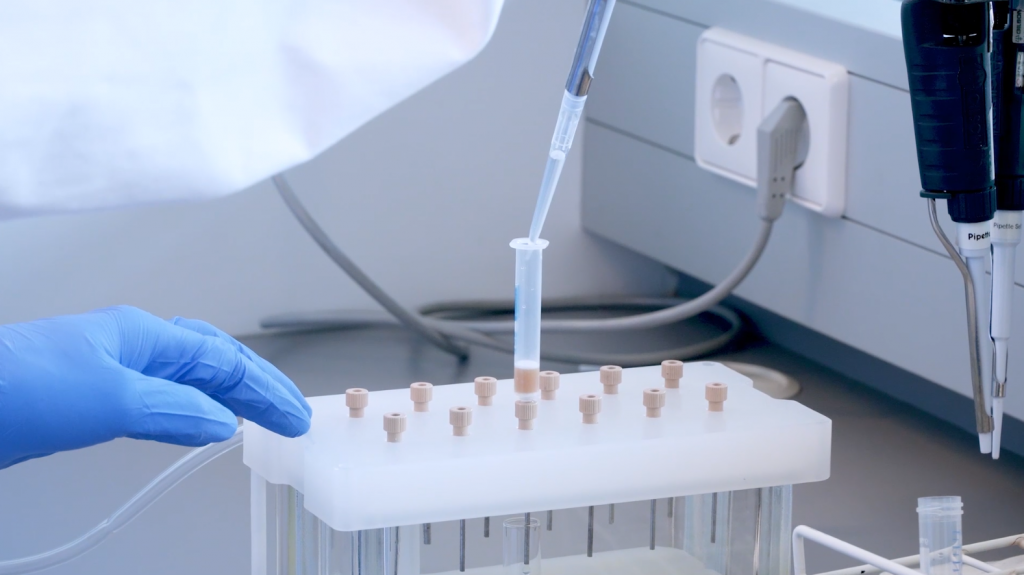
Solid phase extraction is a sample cleanup method which can be adapted to almost any analyte, simply by changing the stationary phase of the SPE cartridge. In this video, a reverse phase cartridge is used to retain parabens from an aqueous sample. By adjusting pH and using various solvents, the parabens are then eluted in acetonitrile for downstream analysis. This video was recorded to introduce students to SPE cartridges, vacuum manifolds, and to demonstrate proper techniques.
- Tineke Bijl
-
(0)
- 0 enrolled students
Description
Non-interactive video download link (mp4).
The script that has been used to create the video shown above can be downloaded as excel script file.
In the lab reverse-phase (RP) SPE cartridges will be available.
What solvent would you like to use to equilibrate the SPE column?
Solvent: [: [acetonitrile / deionized water / methanol / tetrahydrofuran / acidified water]]
- Feedback if acetonitrile / methanol / tetrahydrofuran
The purpose of this step is to equilibrate the column to the right pH that ensures optimal binding of the analytes to the stationary phase. How can this be achieved with an organic solvent?
- Feedback if deionized water
With this type of column, ions don’t interfere with the retention of the analytes. Therefore you do not need to use deionized water.
Feedback if Correct
You have chosen to equilibrate the column with acidified water, the solution of 0.3M HCl.
In the lab reverse-phase (RP) SPE cartridges will be available.
What solvent would you like to use to condition the SPE column?
Solvent: [solvent]
- Acetonitrile (correct)
You have chosen to condition the column with acetonitrile. - Deionized water (incorrect)
The purpose of this step is to wash hydrophobic impurities from the column material. How can you achieve this with a hydrophilic solvent? - Methanol (correct)
You have chosen to condition the column with methanol - Tetrahydrofuran (incorrect)
Tetrahydrofuran would be suitable because it is apolar. However, it is quite toxic. Avoid the use of toxic substances if good alternatives are available. - Acidified water (incorrect)
The purpose of this step is to wash hydrophobic impurities from the column material. How can you achieve this with a hydrophilic solvent?
Water (pH 7) (incorrect)
The purpose of this step is to wash hydrophobic impurities from the column material. How can you achieve this with a hydrophilic solvent?
In the lab you will use prefabricated SPE cartridges. These cartridges come with many types of solid phase material, four different SPE principles are listed below. Indicate the properties of these columns a by dragging the answer options and combining to a correct answer:
- Negatively charged column material (-)
Cation exchange SPE cartridge
- Positively charged column material (+)
Anion exchange SPE cartridge
- Polar column material
Normal-phase (NP) SPE cartridge
- Non-polar column material
Reversed-phase (RP) SPE cartridge
Feedback if correct: Correct answer
There are two types of Solid Phase extraction, making use of the polarity (thus hydrophobicity) of molecules, or based on the charge (ionic strength) of molecules.
Feedback if Normal-phase (NP) SPE cartridge or Reversed-phase (RP) SPE cartridge incorrect:
Normal-phase and reverse-phase chromatography (chromatography meaning separation) are both based on polarity.
In normal-phase chromatography the stationary phase is hydrophilic.
In reverse-phase, the stationary phase is hydrophobic. How do these translate to polarity?
Feedback if Cation exchange SPE cartridge or Anion exchange SPE cartridge incorrect
You did not indicate the right column materials for one or both of the ion exchange columns. The cation/anion term refers to the molecules that will bind to the column material, so these have opposite charge from the column material.
- In Solid Phase Extraction you want the [parabens / mobile phase /solid phase / urine ] to bind to the column material and [parabens / mobile phase /solid phase / urine] to flush through.
Feedback if incorrect: Incorrect, this is not what you want in solid phase extraction. The purpose is to extract the components of interest from a mixture. What are you interested in? And what is the mixture?
- Therefore the column should be conditioned to make sure the analytes ‘rather’ [bind to the solid phase/ move along with the mobile phase] than [bind to the solid phase/ move along with the mobile phase].
Feedback if incorrect: Your second sentence is incorrect. You want your analytes to stay behind in the column so that you can separate from any other components in the mixture.
Feedback if correct
The solid phase and mobile phase can be manipulated to ensure that your analytes bind to the material whilst other components are washed away. Therefore you have to ensure the right starting conditions.
Why do you think the pH of the SPE cartridge should be acidic?
- This ensures that the parabens are all neutral
Correct = yes
- This ensures that the parabens are all negatively charged
Correct = no
Go back and check the pKa’s of these parabens, and evaluate what charge you expect them to have at an acidic pH.
- This ensures that the parabens are all positively charged
Correct = no
Go back and check the pKa’s of these parabens, and evaluate what charge you expect them to have at an acidic pH.
- To increase paraben water solubility
Correct = no
The solubility of the parabens is not a concern at these low concentrations.
- To decrease paraben water solubility
Correct = no
The solubility of the parabens is not a concern at these low concentrations.
- To increase binding affinity of the parabens with the column material
Correct = yes
- To decrease binding affinity of the parabens with the column material
Correct = no
You chose a wrong option, of course it depends on the column material if this step actually leads to increase binding affinity. However, as the purpose is to extract these parabens from the mixture, you want increased binding affinity.
Feedback if correct
The low pH ensures that the stationary phase and parabens remain protonated (remember their pKa values!). This allows them to bind effectively, as the parabens have a higher affinity for the non-polar SPE material than the polar mobile phase.
What is present in the column before the washing step, and what is present after? And what is present in the flow-through?
- Present in column before washing
- Column material
- Parabens
- Sample molecules with higher binding affinity to the column material than the parabens
- Sample molecules with lower binding affinity to the column material than the parabens
- Present in column after washing
- Column material
- Parabens
- Sample molecules with higher binding affinity to the column material than the parabens
- Present in washing flow-through
- Sample molecules with lower binding affinity to the column material than the parabens
- Washing solution
Feedback if correct
During the washing, any molecules that have low binding affinity to the column material will be washed away.
Feedback if Present in column before washing is incorrect
Your answer for what is present in the column before washing is incorrect. At this point, the sample is loaded on the column.
Feedback if Present in column after washing is incorrect
Your answer for what is present in the column after washing is incorrect. At this point, any unwanted molecules will have washed away whilst you have to make that your target molecules stay on the column.
Feedback if Present in washing flow-through
Your answer for what is present in the flow-through is incorrect. Carefully look at what was present before and after washing. The difference is what is present in the flow-through, plus the washing solution of course.
In the lab reverse-phase (RP) SPE cartridges will be available.
What solvent would you like to use to wash the SPE column?
Solvent:
- acetone
The purpose of this step is to wash away as many compounds as possible without losing the analytes. As your analytes are apolar, and the stationary phase is as well, washing with an organic solvent will lead to loss of analytes! - deionized water
With this type of column, ions don’t interfere with the retention of the analytes. Therefore you do not need to use deionized water. - methanol
The purpose of this step is to wash away as many compounds as possible without losing the analytes. As your analytes are apolar, and the stationary phase is as well, washing with an organic solvent will lead to loss of analytes! - tetrahydrofuran
The purpose of this step is to wash away as many compounds as possible without losing the analytes. As your analytes are apolar, and the stationary phase is as well, washing with an organic solvent will lead to loss of analytes! - acidified water
You have chosen to wash the column with acidified water. - water (pH 7)
With a pH this high, part of the analytes will become ionized and partition itself over the aqueous layer. This is exactly what you want to avoid as you want the analytes to stay on the solid phase at this point!
In the lab reverse-phase (RP) SPE cartridges will be available.
What solvent would you like to use to elute the analytes from the SPE column?
Solvent:
- acetonitrile
You have chosen to elute the analytes from the column with acetonitrile. - deionized water
The purpose of this step is to elute the hydrophobic analytes from the column material. How can you achieve this with a hydrophilic solvent? - methanol
You have chosen to elute the analytes from the column with methanol. - tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran would be suitable because it is apolar. However, it is quite toxic. Avoid the use of toxic substances if good alternatives are available. - acidified water
The purpose of this step is to elute the hydrophobic analytes from the column material. How can you achieve this with a hydrophilic solvent? - water (pH 7)
The purpose of this step is to elute the hydrophobic analytes from the column material. How can you achieve this with a hydrophilic solvent?
| Condition & equilibrate SPE column | ||
| 1 | Attach the column to the vacuum manifold. Pipet 1 mL of the chosen solvent into the SPE column. You will need to coordinate with other groups to share the vacuum manifolds. You have chosen to condition the column with methanol. | |
| 2 | Pipet 1 mL of the chosen solvent onto the SPE column. You have chosen to equilibrate the column with water of pH 3. | |
| Load sample on SPE column | ||
| 3 | Add 500 uL of 0.3M HCl in 0.5% methanol to 500 uL of the urine sample. | |
| 4 | Pipet 1 mL of your sample into the SPE column. Generate a low flow rate (approximately 1 mL min–1) using an SPE vacuum manifold. | |
| Wash SPE column | ||
| 5 | Add 1 mL of the chosen solvent to the SPE column. | |
| Elute analytes from SPE column | ||
| 6 | Add 1 mL of the chosen solvent to the SPE column. | |
| 7 | Collect your sample into an eppendorf tube, and dry it in a speed vacuum (Eppendorf concentrator 5301). Please check with a lab assistant before turning on the speed vac. | |
Please make sure that your product exists and valid for this course
- Skill levelInstruction video
- CategoryAnalytical chemistry
Related videos
-
Free
HPLC-UV
Copyright information
This video is created by Leiden Academic Centre for Drug Research (LACDR), Faculty of Science at Leiden University under a open Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. When using this video in its original version please refer to www.labprep.video. When adapting the video, mention the source ‘adapted based on the original version that is created by the labprep.video team’. It is not allowed to use the video for commercial purposes without consultation with the creators. You can contact us via info@labprep.video.