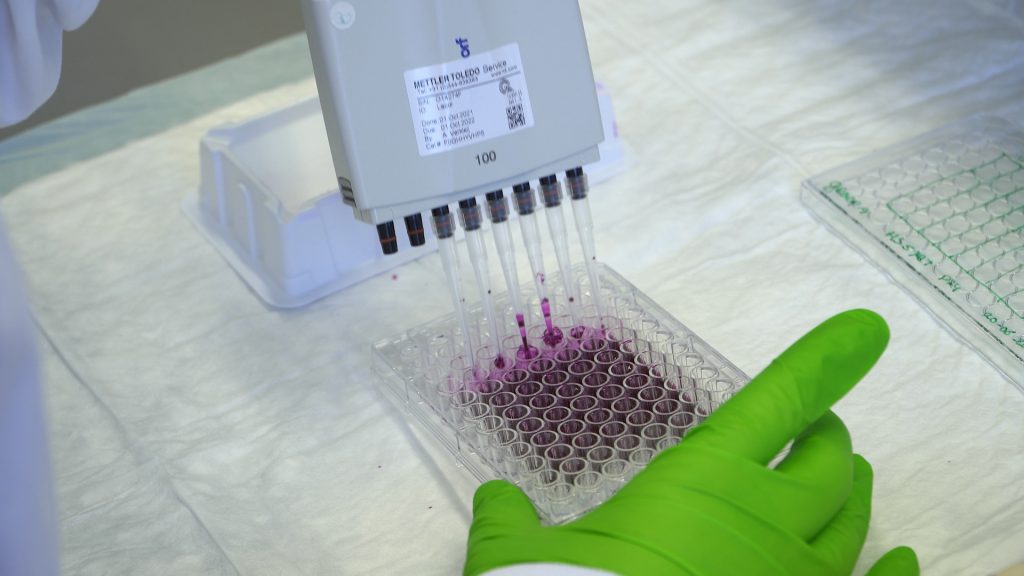
Cell fixation and SRB staining
This video shows how to perform an SRB assay.
- Tineke Bijl
-
(0)
- 0 enrolled students
Description
Non-interactive video download link (mp4).
The script that has been used to create the video shown above can be downloaded as excel script file.
Cell fixation (proliferation) | ||||
| 1 | Retrieve plate from the incubator and note down observations. Try to complete the following steps within 20-30 minutes. | |||
| 2 | Add directly to each well 50 µL 50% TCA solution and place plate in the fridge (4 ⁰C) for 1 hour incubation. | |||
| 3 | Retrieve the plate from the fridge and remove the (toxic!) TCA solution from the plate by pipetting the solution out of each well (use a multichannel pipet). Collect the solution of each well in a reservoir (ask assistants). Hereafter, transfer the TCA solution in the reservoir into a 15 mL tube. | |||
| 4 | Take your plate to the grey box next to the sink (contains demiwater). Wash your plate by dunking it in the grey box. After this, tap out all liquid on the paper tissues next to the sink. | |||
| 5 | Repeat previous step 4 times. Ensure plates are dry and return the plates to the teaching assistant. They will be stored per group in a drawer until tomorrow when you’re doing the next procedure. | |||
Protein extraction | ||||
| 1 | Retrieve your plate from the teaching assistant. Check if they are dry and clean. | |||
| 2 | Add 60 µL of 0.4% SRB solution into each well. Place the lid back on the plate. | |||
| 3 | Shake your plate for 30 min on a plate shaker (at room temperature). | |||
| 4 | Collect the SRB solution from each well back into a tube. This can be reused again. | |||
| 5 | Take your plate to the grey box next to the sink (contains 1% acetic acid). Wash the remaining SRB solution from your plate by dunking it in the grey box. After this, tap out all liquid on the paper tissues next to the sink. | |||
| 6 | Repeat washing with acetic acid 5x. | |||
| 7 | Add 100 µL of 10 mM Tris into each well and incubate for 10 min on plate shaker (at room temperature). | |||
What is the function of the 1% acetic acid solution?
|
What is the correct way of disposing SRB after removal from the plate?
|
Why is it necessary to wash the plate with 1% acetic acid?
|
Which of the following statements is true in regards to the function of adding Tris?
|
What does the SRB solution do?
Feedback if correct: Indeed! SRB solution stains all cellular proteins. Feedback if incorrect: This is incorrect. Read the background information for this technique again and choose another option! |
Which process in the signalling pathway is inhibited by the inhibitors in your experiments?
Feedback if correct: Correct! The phosphorylation of proteins in the Akt or Erk pathways will be inhibited. That is the reason why we will execute a Western Blot. It gives us information about the phosphorylation of these pathways. Feedback if a: Think about which process will be inhibited. Feedback if incorrect: Does the inhibitor work before the receptor or after the receptor? |
On which signalling pathway do the inhibitors have an effect on?
Feedback if correct: Correct! The inhibitors inhibit the phosphorylation of the MEK and Akt proteins which affect their own signalling pathway and the gene expression of proteins involved with migration, proliferation and resistance. Feedback if incorrect: Two of the options are correct. Look up which inhibitor affect the ERK and Akt pathway and how they affect these pathways? The information can be found in the provided datasheets. |
Before starting an experiment with live cells it is important to check your cells with a microscope. Select everything that you should check before starting your experiment:
Feedback if correct: That is correct. As you can see, there are a lot of factors that could affect your experiment. It is important to write down every irregularity when checking your cells. When your data don’t match your expectations, you can trace back the cause by looking it up in your notes. Feedback if c: What is inside the outer wells? Feedback if e: Inhibitor is not always present when the cells should be checked. |
For the combi inhibitor condition, the working concentration is twice the final concentration compared to the single inhibitor condition. What is the reason for that?
|
Above you can see your plate layout for the plate you will use for SRB and IF (1 plate each). Since you need similar conditions for both experiments, you can make inhibitor volumes for both plates together. Calculate the volume needed of inhibitor and RPMI complete medium to make your solution for the lanes with “Inhibitor A” to fill up both plates (note that both cell lines will be treated with this inhibitor). The stock concentration is 2 mM, the target concentration is 1µM and each well can hold 100 µL of liquid. On top of the amount that you need to fill all wells, add 6 wells of volume to your calculation to compensate for pipetting errors. Note: this is an example calculation for practice, you will not do this during the actual experiment, for that you will find novel instruction in the “protocol” tab. We need __d__ µL of stock solution We need __c__ µL of RPMI
Feedback if d > 2998.5 and d < 3000 and c = 1.5: Very good! you calculated it correctly. |
Download zip to import in LabBuddy.
Please make sure that your product exists and valid for this course
- Skill levelIntroduction video
- CategoryCytochemistry
Related videos
Copyright information
This video is created by Leiden Academic Centre for Drug Research (LACDR), Faculty of Science at Leiden University under a open Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. When using this video in its original version please refer to www.labprep.video. When adapting the video, mention the source ‘adapted based on the original version that is created by the labprep.video team’. It is not allowed to use the video for commercial purposes without consultation with the creators. You can contact us via info@labprep.video.